How Radiology Simulators Are Transforming Diagnostic Education?
- surgeonslab1
- Oct 25, 2024
- 4 min read
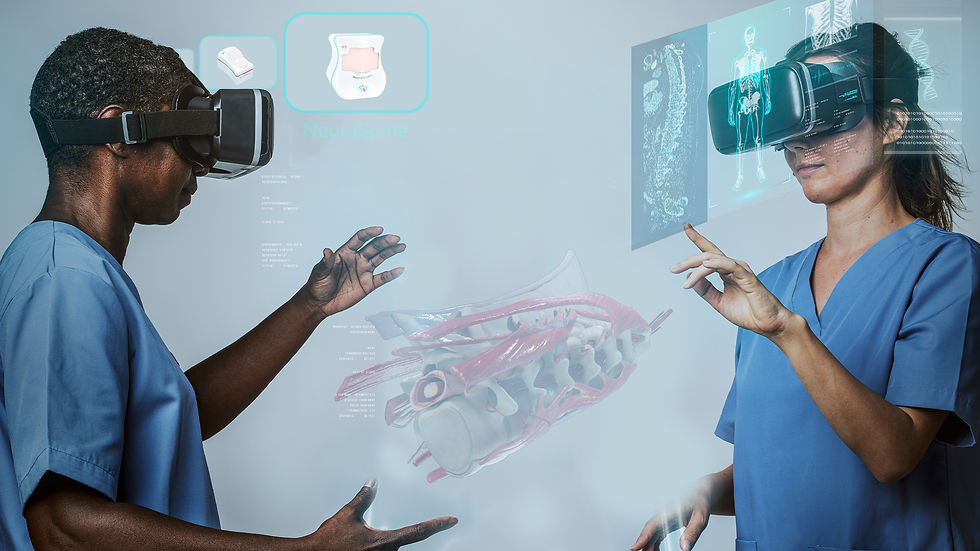

Technology has surely played an important role in the increasingly developing field of medical education. This includes the development of training and preparing potential healthcare professionals. Diagnostic radiology, like numerous other disciplines, has experienced significant growth through radiology simulator software. This technology changes the way radiology students and residents practice and learn; far more interactive and immersive approaches are introduced to the students and residents.
This article looks into the role that radiology simulators play in their benefits and the transformation witnessed in diagnostic education.
The Rise of Radiology Simulators
Radiology simulators are high-tech, computer-based systems that can mimic or almost perfectly repeat scenarios in real-life diagnostic settings. Simulation provides a virtual environment where learners may practice and hone their skills in image interpretation, making diagnoses, and enhancing clinical decision-making skills. It is no new concept, but simulation-based learning in radiology education is more popular today than in years past.
Hands-on exercise with real patients supplements the conventional method of teaching radiology, which is mostly through lectures and textbook knowledge. Although this method has advantages, it often encounters problems such as unavailable patients, low ethical requirements, and lower immediacy. Radiology simulators attempt to bridge the gap by creating a safe and controlled learning environment.
Benefits of Radiology Simulators in Diagnostic Education:
Realistic and Immersive Learning Experience
Radiology simulators create remarkably lifelike and immersive learning environments. Advanced imaging datasets, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, are commonly used to model various clinical cases. The learner can then engage with these images, operate on them, or make diagnoses as if they were dealing with real patients. This realism promotes increased engagement and allows students to learn more about anatomical structures and pathologies.
It, for instance, boasts one of the most well-known training software for surgeons, such as SurgeonsLab. Such software combines all types of simulation modules in radiology under one roof. This, therefore, produces a wide clinical spectrum of cases, including various anatomical regions and pathologies. The various imaging modalities can be tested while making measurements and annotating within an intuitive interface. Interaction at this level ensures active engagement with the learning process.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy and Confidence
The highest objective of the radiology curriculum is to enhance diagnosis and decrease error levels; radiology simulators will form the crux of achieving this end. A large library of clinical cases will expose students to a vast spread of pathologies with infrequent exposure to rare conditions, truly exposing them to whatever conditions they may encounter. Such exposure helps in differential diagnosis and helps develop a complete understanding of various diseases and their relevant yet subtle abnormalities.
Moreover, radiology simulators give instantaneous responses to diagnostic choices. Such students get immediate assessments about their interpretations so that they can identify their weak areas and correct mistakes without criticism. The action cycle enhances their confidence and encourages self-directed learning. As a result, the students are prepared to deliver accurate diagnoses and better evaluate real-life clinical practice.
Safe and Ethical Training Environment
One of the major issues with medical education is a significant concern: ethical considerations. At this point, one has to carry out most of the work with real patients. Using simulators in radiology reduces the patient's exposure to any invasive procedure or even potential risks of repeated imaging. Thus, learners can now try their techniques on virtual patients, and they can simply make mistakes and learn without harming real-life humans.
With radiology simulators, educators can design standard practice scenarios; students are thus evaluated systematically and equitably. Such standardization provides excellent value when assessing and comparing the learner's performance between or across institutions or programs. It also helps point out where extra training or support would be beneficial.
Improved Time Efficiency and Accessibility
Traditionally, in radiology education, the number of patients and availability of imaging equipment are used as a basis, which naturally limits the cases that students are to review. In radiology simulators, however, access to a large and easily available library of cases can be obtained. With these cases, learners may access them at any given time, anywhere; thus, one may study and practice at one's own pace.
Moreover, radiology simulators are flexible in terms of learning style. For instance, one can learn a particular anatomy or pathology while focusing on a specific region—a preference that some students will have. Thus, the learning experience can be modified in congruence with student needs. This has improved retention and enabled learners to focus on areas they identified as needing more attention.
To Conclude
Radiology simulators transform the best surgical tech programs by offering a safe, highly immersive environment in which to train. They bring plenty of advantages in this process, including higher accuracy in diagnosis, greater confidence concerning condition diagnostics, and further personalization of learning experiences. Incorporating AI only enhances these features of radiology simulators, thus making them an unavoidable resource in medical education for students, residents, and practicing radiologists.
The outcome will be increasingly sophisticated radiology simulators, which will further close the gap between theory and practice. The future of diagnostic education seems bright; it depends on getting people familiarized with radiology simulators, which will allow for the appropriate modulation of the next generation of radiologists and improve patient care accordingly.